Join us on our journey towards renewable energy excellence, where knowledge meets innovation.
Virtual Power Purchase Agreements (VPPAs) are on the rise in the electricity market due to the possibilities they create for both offtakers and producers.
In this post, we explain why these market participants are likely to achieve a higher success rate through VPPAs.
A bilateral agreement between a renewable energy producer and an offtaker that doesn't involve the physical delivery of the traded electricity.
Also known as Financial PPA, Synthetic PPA, or Contracts for Difference (CfD).
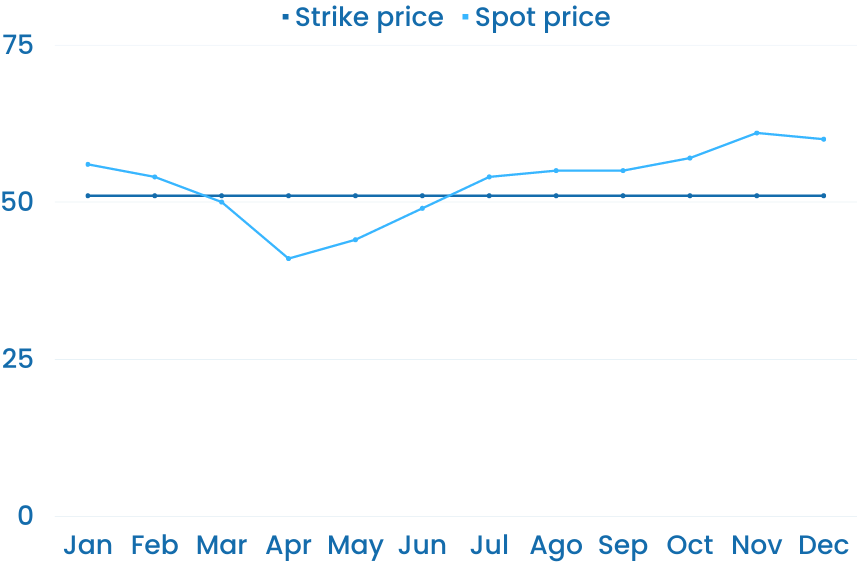
First, a producer agrees to sell an amount of its electricity to an offtaker for a fixed price (the strike price).
Second, the electricity is sold through a market agent in an energy exchange for the spot price.
Third, the power producer and offtaker settle their positions according to the differences between the strike and spot prices.
When the spot price is below the strike price, the buyer pays the difference to the producer.
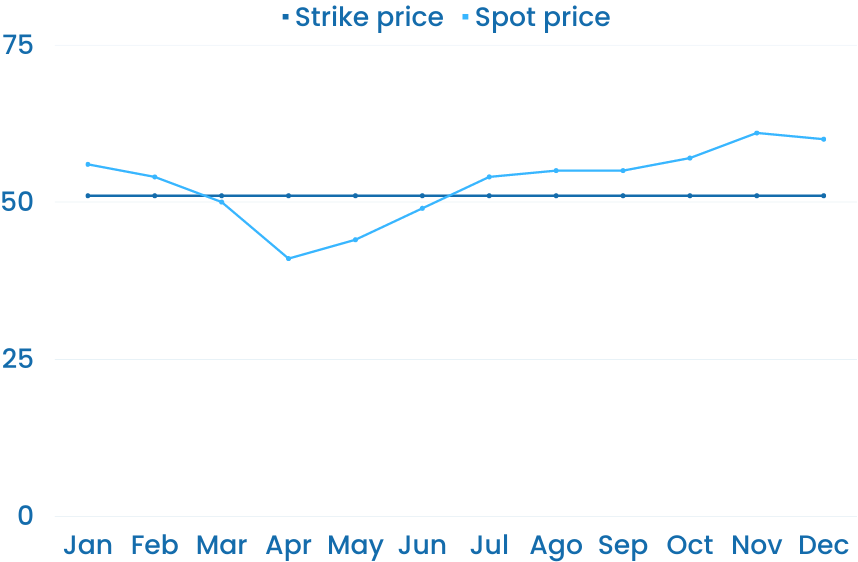
Whenever the spot price is above the strike price, the producer pays the difference to the buyer.
Increased flexibility for market participants
Also, check out the video we elaborated on this topic:
Synertics provides advisory services and develops digital data-driven solutions for the energy industry with the purpose of driving productivity and transferring knowledge.

Insights
3rd Mar, 2026
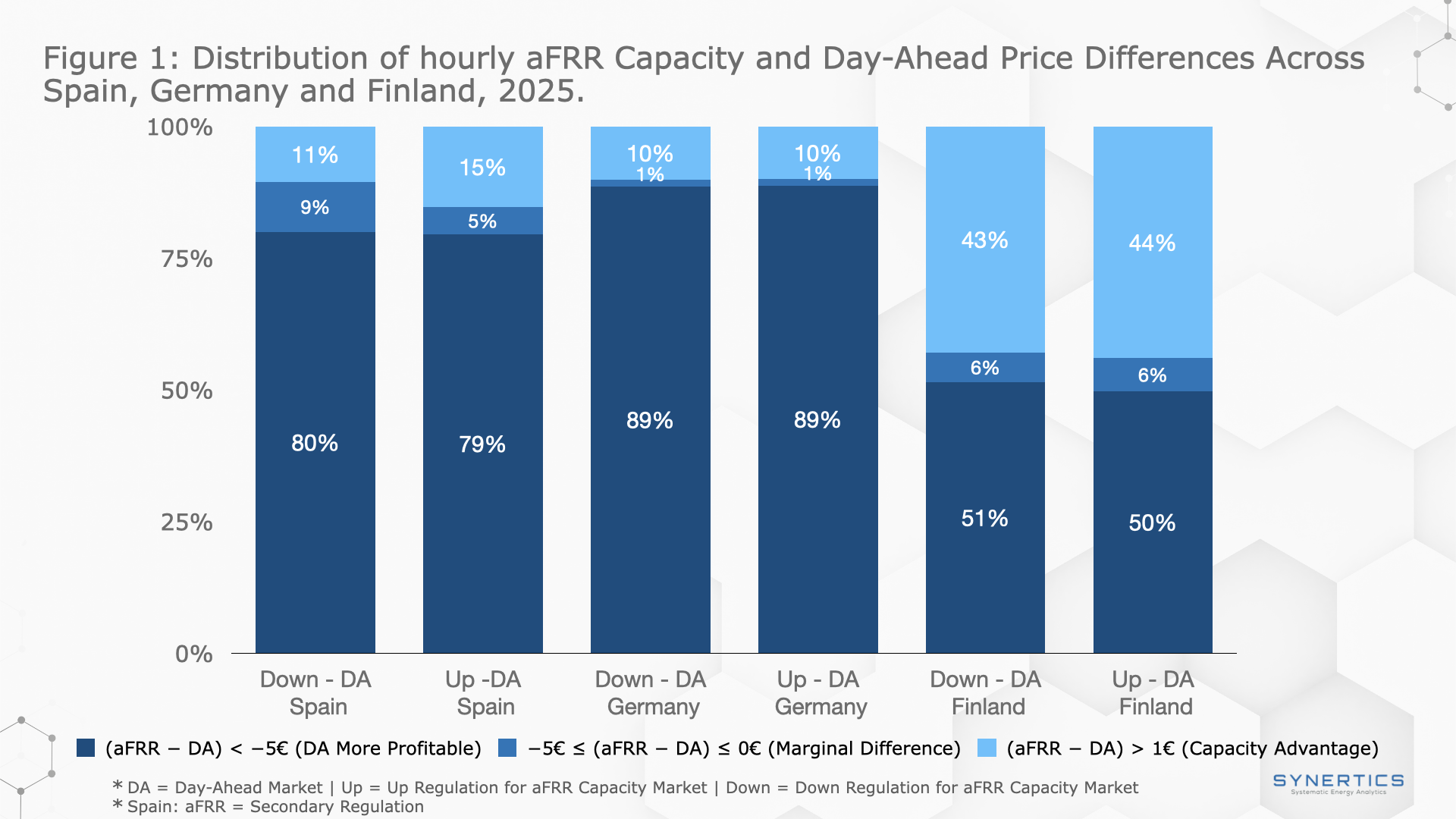
Insights, Market-trends
27th Feb, 2026

Insights
29th Jan, 2026