Join us on our journey towards renewable energy excellence, where knowledge meets innovation.
The final price of a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) is influenced by several key factors such as capture prices, futures, guarantees of origin and volume, price and cannibalisation risks. Quantifying each of these drivers while reflecting market trends and players' expectations can be challenging. In this article, we will identify and explain the key drivers used in Synertics’ methodology to estimate the fair value PPA price for a location- and technology-specific asset.
The waterfall chart in Figure 1 highlights the primary pillars that will impact the fair value of a PPA price. Please note that the values shown are only illustrative but exemplify the process. 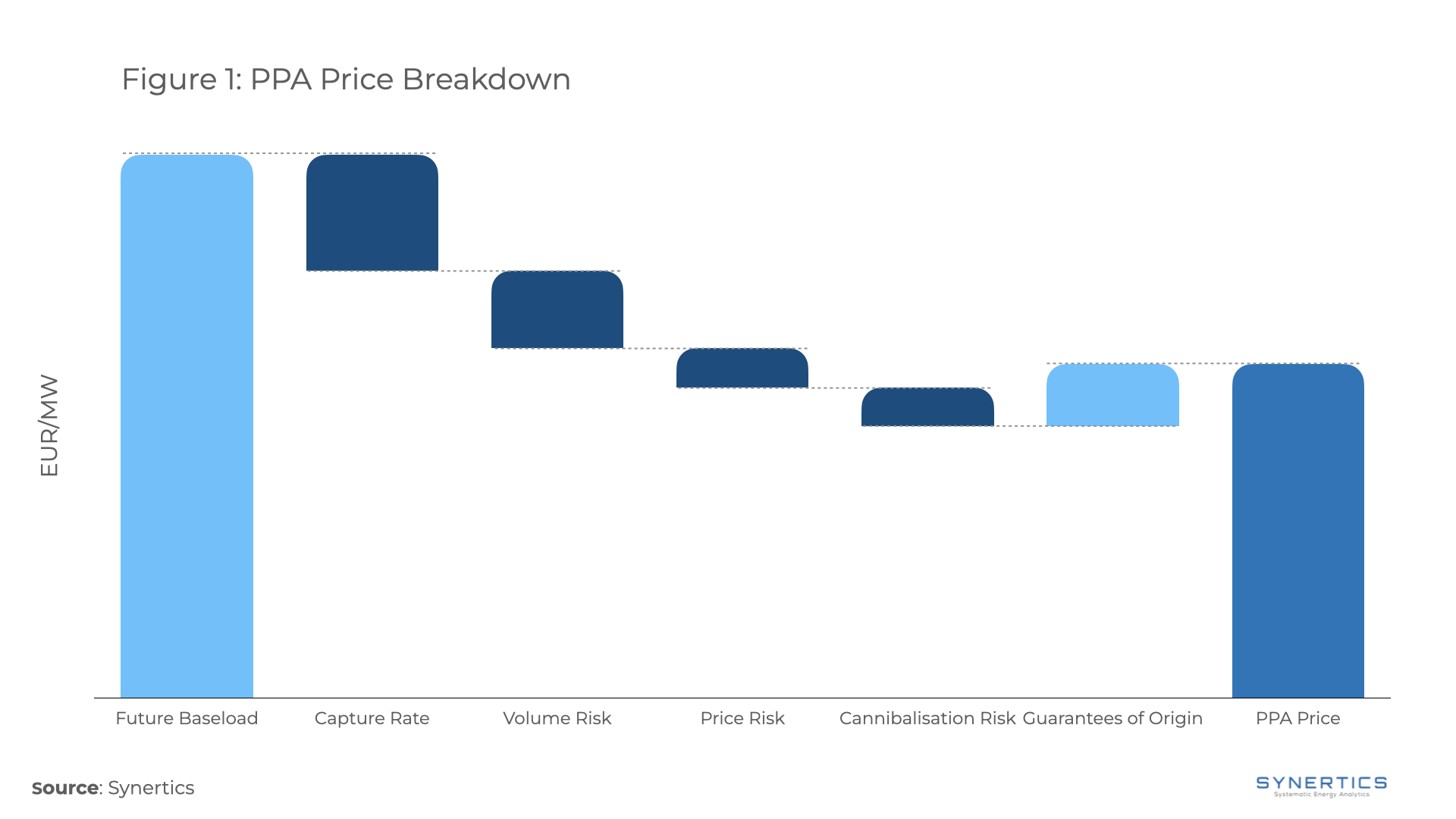
Firstly, the country-specific future baseload prices are used to compute a reference baseload price. Adjustments are then made by subtracting capture rate, volume risk, price risk, and cannibalization premiums from this reference In the final step, the projected future value of Guarantees of Origin (GoOs) over the contract duration is added, revealing the final fair value of the PPA price.
It is important to note that the methodology described here does not include soft drivers that impact the price, which depends on more in-depth PPA negotiation such as balancing cost, negative prices settlements, offtaker bankability, etc.
Baseload Futures
Futures contracts play a key role in hedging against market volatility. For PPA stakeholders, futures reflect the market's valorisation of electricity predictability. Our methodology utilises futures contracts for baseload calculations due to the following factors:
Capture rate discount
Capture prices represent the market price that producers can expect to earn for their electricity. This is a crucial input when calculating PPA prices, as it directly impacts a project's estimated revenue. These prices are based on several factors:
To tailor the PPA to each specific project, we use its specific production profile and the day-ahead prices to reflect how the average price earned by a power plant compares to the baseload price of electricity in the day-ahead market.
You can learn more about capture prices and calculate them for your asset by reading this article.
Volume risk discount
Volume risk is the uncertainty of predictability in forecasting how much energy will be generated or consumed within the PPA term. This unpredictability affects the price within the agreement on a wide range of levels:
By using the asset’s location and its corresponding historical weather data, we can quantify the expected volatility of the power plant and reflect these risks in the price.
Price risk discount
Price risk discount accounts for the uncertainty in future electricity prices. This discount impacts PPA pricing and is influenced by several factors:
Cannibalisation risk discount
Cannibalisation risk discount reflects the risk that by adding more capacity of a specific technology to the electricity market it might further drive down the capture rates. To assess this risk, we use renowned databases describing expected future renewable installed capacity installations to quantify how much we expect the capture rate to depreciate over the PPA duration.
Guarantees of Origin
Guarantees of Origin (GoOs) are renewable energy certificates that certify that electricity was generated from renewable sources.This adds significant value to a PPA especially as sustainability targets become more stringent. The increasing demand for GoOs makes securing them through a PPA highly attractive for consumers.
Similar to the futures market for electricity, the futures market for GoOs provides valuable insights into the pricing trends of these certificates. At Synertics, we analyze these trends to assess their impact on the final PPA price. To understand the fundamentals of Guarantees of Origin and other Renewable Energy Certificates, read this article, and for a deeper dive into their growing role in the European market, explore this article.
Soft drivers
Additionality: The concept of additionality can play a role in PPA pricing. PPAs that directly contribute to the creation of new renewable energy generation capacity are increasingly in demand. PPAs financing the construction of new wind or solar farms command a premium compared to those that simply transfer existing renewable energy certificates. This premium reflects the buyer's willingness to pay for the tangible environmental impact of supporting new renewable energy development, which directly contributes to decarbonisation efforts.
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM): The EU's CBAM is set to become a key driver of PPA pricing. Designed to prevent carbon leakage, the CBAM will impose a carbon levy on imports of certain goods from countries with weaker carbon regulations. This encourages companies to reduce their carbon footprint, making renewable energy sourcing through PPAs a strategically advantageous option. To minimise potential CBAM liabilities, companies may be willing to pay a premium for PPAs that ensure their electricity comes from demonstrably low-carbon sources, further impacting PPA prices.
Environmental Concerns and Reputation: Growing public awareness of climate change and sustainability drives companies to prioritise decarbonisation and demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices. PPAs offer a powerful way to showcase environmental stewardship. The desire to enhance reputation and meet stakeholder expectations for sustainability can influence PPA pricing. Slightly higher PPA prices may be accepted to secure renewable energy from projects with strong environmental and social credentials, thereby enhancing brand image and demonstrating a genuine commitment to sustainability.
Conclusion
PPA pricing is shaped by a dynamic interplay of factors, including market-driven capture prices, hedging through futures contracts, the added value of Guarantees of Origin, volume and price risk uncertainties, and other soft driver factors. In the case of a pay-as-produced structure, the offtaker is bearing all risks and needs to account for them when computing a PPA price.
As the renewable energy market continues to evolve, understanding these price drivers is essential for securing long-term success in the PPA space. Depending on the desired PPA structure, quantifying each driver is essential to evaluate the fair price of a PPA.
If you're looking for expert guidance in navigating PPA pricing and structuring the right agreement for your needs, talk to our team at Synertics, we’re here to help you make informed, strategic decisions.

Insights
11th Mar, 2026

Insights
3rd Mar, 2026
Insights, Market-trends
27th Feb, 2026