Join us on our journey towards renewable energy excellence, where knowledge meets innovation.
The European Union experienced a significant drop (-90TWh) in electricity demand from 2021 to 2022, driven by a complex interplay of factors. We’ll take a closer look at them.
The primary driver was the energy crisis triggered by the Russian invasion of Ukraine, which led to sanctions on Russian oil and gas supplies and subsequently caused energy prices to surge. This sudden disruption in energy supply chains significantly impacted electricity generation and distribution, prompting a decrease in overall electricity demand as businesses and consumers grappled with higher costs.
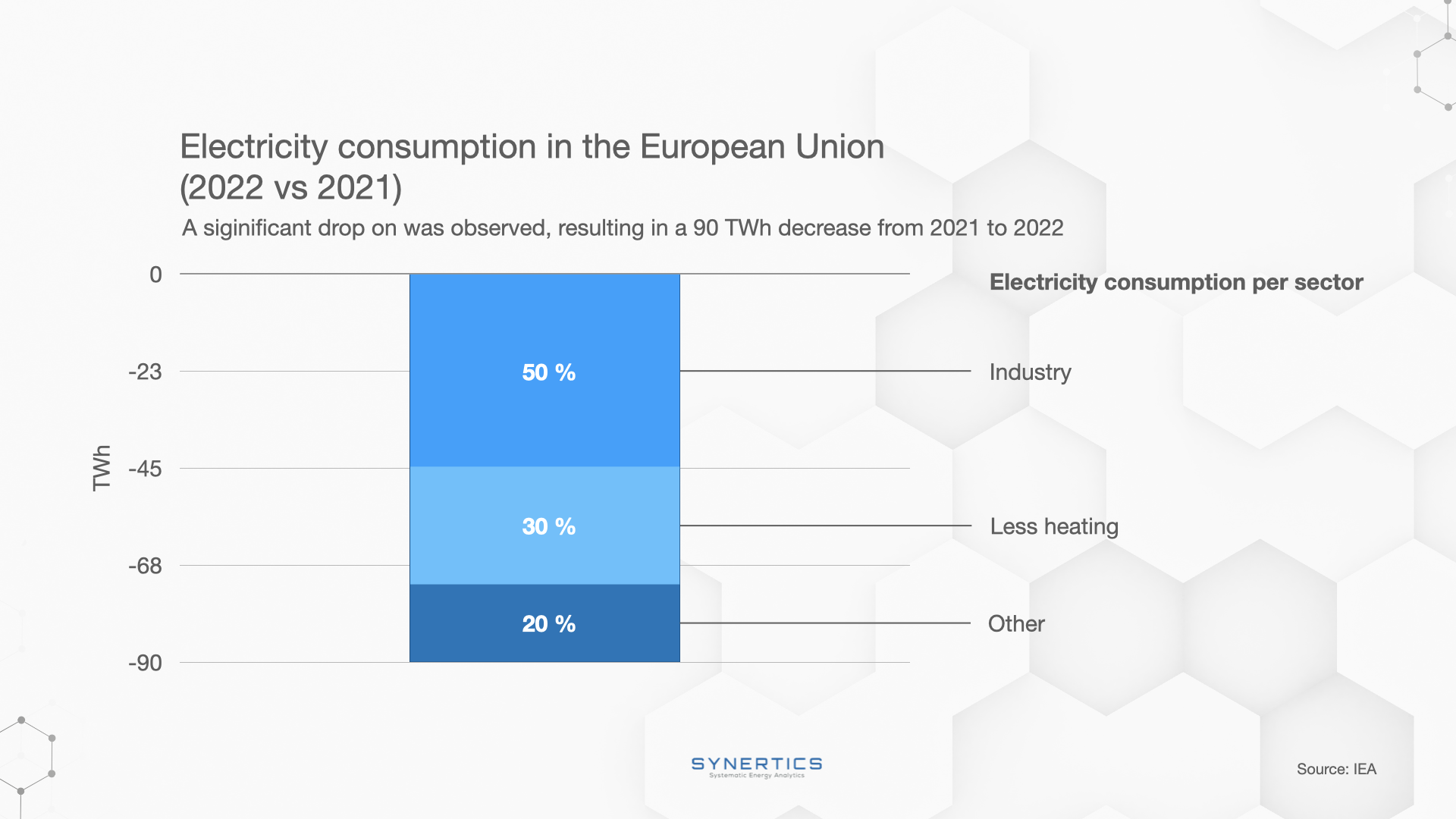
While the weather is traditionally a significant factor in electricity demand fluctuations, the analysis revealed that the weather's impact was less pronounced than anticipated. The unusually mild winter (leading to less heating required) partially offset the effects of a hotter summer, which necessitated additional cooling needs. The net effect of these weather drivers was not as substantial as other contributing factors in the demand drop.
A substantial portion of the electricity demand reduction was attributed to non-weather-related drivers. Notably, almost two-thirds of the decline were linked to decreased demand from energy-intensive industries, which were particularly sensitive to high energy prices. These industries, facing affordability challenges and uncertain electricity prices, made decisions to curtail production or even relocate their operations to regions with more stable electricity prices, primarily Asia. The residential and services sectors also played a role, as behavioral changes, voluntary energy savings, affordability concerns, and efficiency improvements contributed to the decline in electricity consumption.
While the energy crisis arising from the Russian invasion of Ukraine served as the backdrop for last year’s 3.2% electricity consumption drop in the EU, the influence of weather was less significant than anticipated.
This marked the second most significant decline since the global financial crisis in 2009, surpassed solely by the substantial fall in 2020 as a result of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Non-weather-related factors, including reduced demand from energy-intensive industries, behavioral changes in various sectors, government incentives, and efficiency improvements, played a substantial role as well.
However, the concerning outcome was the departure of industries from Europe, enticed by more stable energy costs in other regions. This phenomenon led to a potential loss of jobs, decreased economic activity, and challenges for the EU’s economy. Therefore, we strongly believe that securing a stable electricity market will be crucial in addressing these challenges and shaping the EU's energy landscape in the coming years.
Synertics provides advisory services and develops digital data-driven solutions for the energy industry with the purpose of driving productivity and transferring knowledge.

Market-trends
4th Mar, 2026
Insights, Market-trends
27th Feb, 2026

Market-trends
6th Feb, 2026