Join us on our journey towards renewable energy excellence, where knowledge meets innovation.
Understanding the formation of electricity prices under the Merit-Order principles.
In the search for understanding energy markets, we will explore how the merit order establishes electricity prices under consideration of market specific generation capacities. As the energy market is constantly changing, one must be in tune with key terms and new knowledge about how things work to better understand what’s happening in real-time and make smarter decisions.
The merit order defines the sequence in which power plants produce and deliver electricity. The sequence is ordered by different sources of generation capacities with the lowest marginal costs, thus optimizing the economic aspects in the supply of electricity.
The Merit-Order curve visualizes the sources of electricity particular to a certain market on a capacity (in MW) and the respective marginal costs. Marginal costs define the cost for each additional unit of produced electricity (in €/MWh). The capacities with the lowest marginal costs are prioritized, which leads to an efficient selection of electricity supplies and focuses on keeping electricity generation costs low.
The graph below is based on a Merit-Order curve constructed by Synertics for TransnetBW based on a generation electricity price forecast in the year 2050.
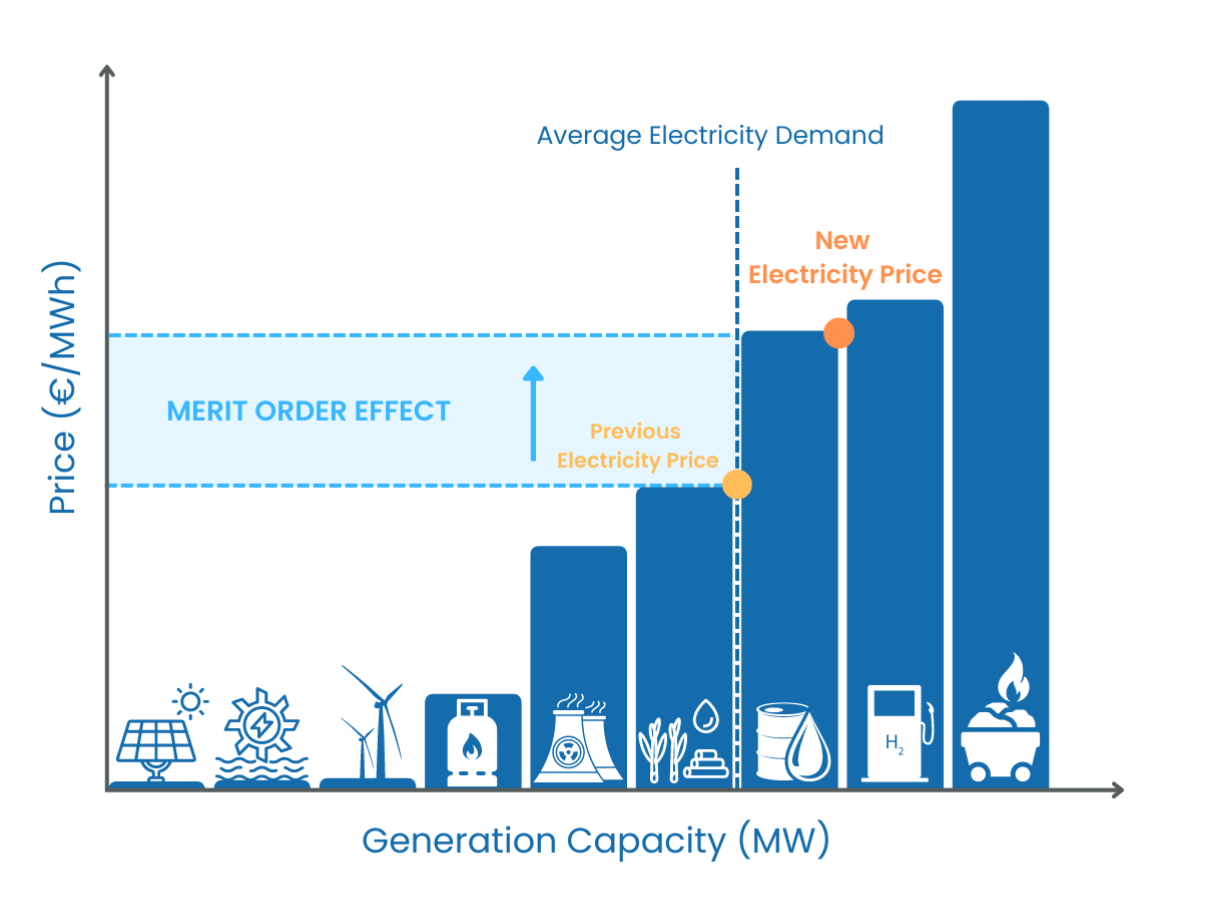
Sources of electricity generation with the lowest marginal costs, e.g. renewables are activated first, before accessing electricity generation capacities with higher marginal costs such as lignite and gas-powered power plants.
Several factors need to be considered when projecting a Merit-Order curve, such as hourly demand, location-specific energy mixes, and marginal costs. Luckily, there are tools that can facilitate the understanding of what’s in play. With an industry-leading PPA tool, it becomes much easier to understand the value of assets in accordance with respective technologies and markets.
As solar and wind technologies play an increasingly relevant role in generation mixes, understanding various revenue hedging options through power purchase agreements becomes empirical. Synertics PPA Evaluation Tool helps asset and investment managers transparently and efficiently evaluate revenue and risk relationships of various PPA options to maximize the value of assets.
Synertics provides advisory services and develops digital data-driven solutions for the energy industry with the purpose of driving productivity and transferring knowledge.

Insights
11th Mar, 2026

Insights
3rd Mar, 2026
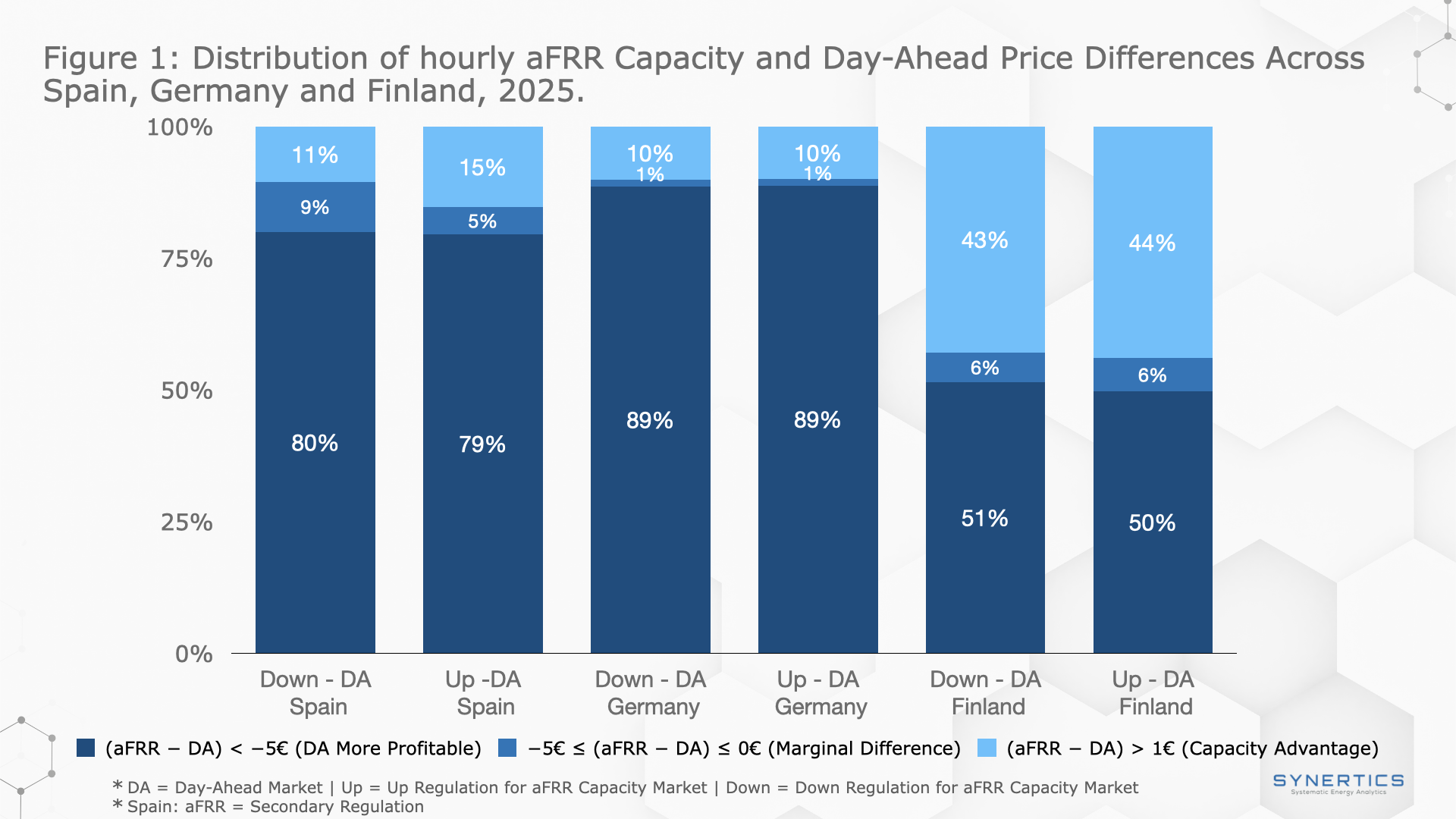
Insights, Market-trends
27th Feb, 2026